Imagine two titans, locked in an epic battle for e-commerce supremacy, Alibaba vs Amazon. In one corner, we have Amazon – the undisputed king of online retail, dominating the Western world with its vast product selection and lightning-fast delivery.
But don't count out its challenger just yet. In the other corner stands Alibaba, the Chinese juggernaut that has already conquered the massive market in its homeland.
These two behemoths have been circling each other for years, each looking to expand into the other's territory. But how do they really stack up against one another? What are their key differences and similarities?
And most importantly, which one will emerge victorious in this clash of the e-commerce giants?
Alibaba Vs Amazon
| Aspect | Alibaba | Amazon |
|---|---|---|
| Headquarters | Hangzhou, China | Seattle, Washington, USA |
| Founded | 1999 | 1994 |
| Founder(s) | Jack Ma | Jeff Bezos |
| Business Model | B2B e-commerce marketplace connecting buyers and sellers | B2C e-commerce retailer selling directly to consumers |
| Key Platforms | Alibaba.com (B2B), Taobao (C2C), Tmall (B2C) | Amazon.com, Amazon Prime, AWS |
| Revenue Sources | Commission fees, advertising, cloud services, digital media | Online product sales, third-party seller services, AWS, advertising, subscriptions |
| 2022 Revenue | $134.6 billion | $469.8 billion |
| 2022 Net Income | $17.1 billion | $33.4 billion |
| Market Focus | Primarily China, expanding globally | Global, strong presence in North America and Europe |
| Logistics | Does not own warehouses or delivery network, relies on third-party logistics | Owns vast warehousing and delivery infrastructure |
| Payment System | Alipay | Amazon Pay |
| Key Advantages | Dominates Chinese e-commerce market, asset-light model | Massive global customer base, logistics capabilities, diversified revenue streams |
| Key Challenges | Expanding beyond China, competing with established global players | Intense competition, regulatory scrutiny, high operational costs |
Market Dominance
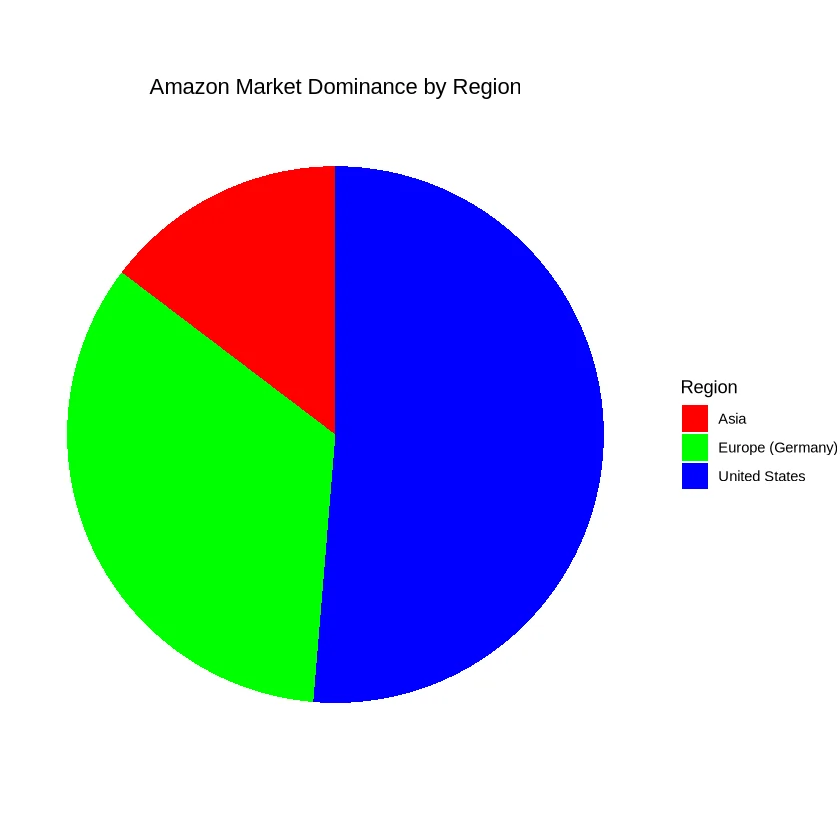
Amazon, with its vast online presence, has established itself as a leading e-commerce platform not just in the United States but also internationally. It has managed to integrate itself into the daily lives of consumers through services such as Amazon Prime, which has a substantial subscriber base including 46.4% of German households.
This subscription-based model has not only fostered customer loyalty but also created a consistent revenue stream for the company.
| Region | Amazon Prime Market Penetration |
|---|---|
| United States | High |
| Europe (Germany) | 46.4% Households |
| Asia | Emerging Presence |
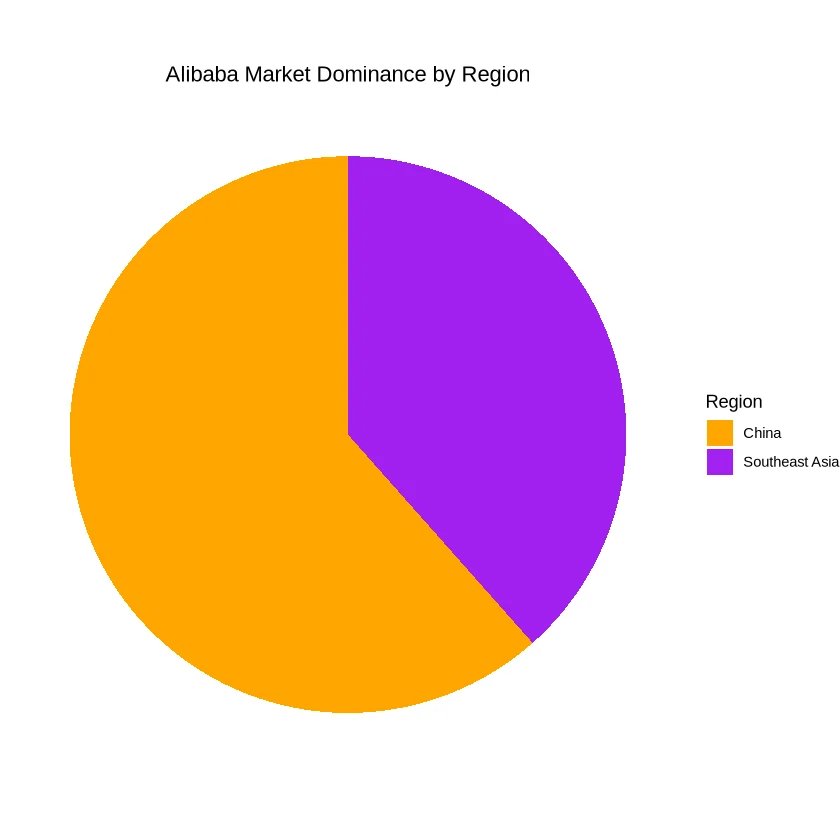
In contrast, Alibaba dominates the Chinese and Southeast Asian markets. With its Southeast Asia arm Lazada, Alibaba is reaching 130 million annual consumers. Alibaba's expansion strategy focuses on regions where e-commerce is still burgeoning, allowing them to shape consumer habits and preferences.
| Region | Alibaba Market Dominance |
|---|---|
| China | Very High |
| Southeast Asia | High |
The dominance of each platform is intricately linked to their strategic focus and understanding of their respective markets.
Technological Advancements
When it comes to technology, both Amazon and Alibaba are at the forefront of innovation, albeit in different ways.
Amazon's technological infrastructure is vast, encompassing everything from cloud computing services to advanced warehousing. The company continues to invest in automation, AI, and machine learning to optimize operations and improve customer interactions.
Alibaba, on the other hand, is making significant strides in technology development and research. With investments in digital assistants capable of handling a massive number of sophisticated customer interactions, Alibaba may well have the potential to outcompete Amazon in certain technological arenas.
The scope of Alibaba's technological advancements is not limited to e-commerce but extends to fintech, cloud computing, and AI-driven logistics.
Business Models
The business models of Amazon and Alibaba are tailored to their strategic objectives and market conditions. They both have changed the e-commerce landscape but in markedly different ways.
Amazon's Model

Amazon's approach to e-commerce is that of a massive retailer, offering both new and used goods, and maintaining an extensive network of warehouses globally to store inventory.
This direct-to-consumer model allows for efficient distribution and quick delivery, a cornerstone of their service promise, especially for Amazon Prime subscribers who enjoy expedited shipping.
Furthermore, Amazon provides a marketplace for third-party sellers, acting as a liaison between these sellers and a vast customer base. Sales through Amazon's platform are subject to a commission, contributing to their revenue. The company extends its reach through its own product lines, such as the Amazon Kindle e-readers, e-books, and a plethora of mobile applications.
| Revenue Source | Description |
|---|---|
| Amazon Prime | Subscription-based service offering free shipping and streaming media. |
| Third-party sales | Commission on sales price for products sold by other retailers on Amazon's platform. |
| Proprietary products | Sales of Amazon's own products, including Kindle and related digital content. |
Alibaba's Model

Alibaba, the dominant force in China's e-commerce sector, functions primarily as a middleman, connecting buyers with sellers on its various websites such as Taobao and Tmall.
Unlike Amazon, Alibaba does not generally maintain a stockpile of goods in warehouses. Instead, it relies on a vast network of sellers to fulfill consumer demand.
Taobao operates akin to eBay, allowing sellers to list items fee-free, with the option to pay for enhanced visibility—thus Alibaba generates significant revenue from advertising. Tmall, conversely, caters to more prominent brands and retailers—like Gap and Nike—and monetizes through annual user fees, sales commissions, and deposits.
| Platform | Seller Fee Structure |
|---|---|
| Taobao | No listing fees; revenue primarily from advertising. |
| Tmall | Annual user fees, sales commissions, and deposits from larger retailers. |
Alibaba has also addressed e-commerce pain points such as transaction security by developing Alipay, a secure payment system ensuring buyer protection. This, combined with ventures into micro-lending, showcases Alibaba's diversification beyond mere e-commerce.
Revenue Generation
The revenue generation mechanisms of Amazon and Alibaba are critical components in understanding the dynamic comparison between Alibaba and Amazon. Both companies have diversified their revenue streams, capitalizing on their platforms to maximize profit.
Amazon's Revenue Streams
Amazon follows an “Asset-Heavy” model, where it sells goods directly, acts as a platform for other retailers, controls its own ecosystem, and earns profits through commissions. A significant part of Amazon's revenue comes from its online storefront, where it retails an array of products ranging from books to electronics.
The company also retains a portion of the sales price as commission from third-party retailers using its platform. Another substantial revenue stream comes from its subscription-based model, Amazon Prime, which provides members with benefits such as expedited shipping and access to streaming media. In Germany, for instance, 46.4% of households are subscribed to Amazon Prime, indicating the service's popularity.
Moreover, Amazon earns revenue through its e-reader, Kindle, along with sales of e-books and mobile applications for Kindle owners. The table below outlines the diverse revenue streams of Amazon:
| Revenue Stream | Description |
|---|---|
| Direct Retail Sales | Sales of products from Amazon's vast online inventory. |
| Third-Party Seller Services | Commissions and fees from marketplace sellers. |
| Amazon Prime Subscriptions | Annual or monthly fees for membership benefits. |
| Kindle and Related Services | Sales of e-readers and digital content. |
For Amazon Sellers and e-commerce entrepreneurs, understanding these revenue streams is crucial for leveraging Amazon FBA, utilizing tools such as the Amazon FBA calculators, and utilizing advertising options with Amazon DSP vs Display Ads.
Alibaba's Revenue Streams
Alibaba's “Asset-light” model, similar to eBay's, connects buyers and sellers while leaving aspects like terms of sales, delivery, and warehouses to the sellers themselves. Alibaba's core business model acts as a facilitator between buyers and sellers through its extensive network of websites.
The largest of Alibaba’s sites, Taobao, allows sellers and buyers to transact without fees, with sellers paying for better visibility on the site's search engine. This is in contrast to Amazon, which generates revenue through commissions on sales from its partner retailers and fees from its Amazon Prime service.
Alibaba also generates revenue from its financial services like Alipay and its micro-lending business. These services complement its e-commerce platforms, providing a comprehensive ecosystem for consumers and businesses alike.
| Revenue Stream | Description |
|---|---|
| E-commerce Platforms | Revenues from search ranking fees and commissions. |
| Financial Services | Income from Alipay transactions and lending services. |
| Cloud Computing | Earnings from Alibaba Cloud services. |
Strategic Differences

While both Alibaba and Amazon are e-commerce giants, their core strategies differ significantly. Amazon's strategy revolves around being a direct retailer, owning inventory, and managing the entire selling process from warehousing to delivery.
In contrast, Alibaba operates as a marketplace platform, connecting buyers and sellers without holding any inventory itself.
Amazon aims to provide an exceptional end-customer experience, investing heavily in logistics and fulfillment infrastructure. Alibaba, on the other hand, focuses on facilitating business-to-business transactions, enabling small businesses and manufacturers to reach a global customer base. This asset-light model allows Alibaba to rapidly expand its reach without the overhead costs associated with Amazon's vertically integrated approach.
Customer Focus
Amazon's customer-centric approach is evident in its commitment to providing a vast selection of goods directly to consumers. It has established a vast network of fulfillment centers to store inventory and ensure swift delivery through its logistics arm.
This approach not only caters to end consumers but also supports a thriving marketplace for third-party sellers, offering them services such as Amazon FBA to ease their selling process. Amazon's focus is on ensuring that customers have a seamless shopping experience, from browsing to delivery.
On the other hand, Alibaba's customer focus is on facilitating a connection between buyers and sellers. Through platforms like Taobao, which commands a significant portion of online purchases in China, Alibaba functions primarily as a middleman that allows transactions to occur without directly handling goods.
This model is particularly advantageous for smaller merchants who are not charged transaction fees but can opt for paid advertising to boost visibility, a revenue stream for Alibaba. For larger retailers, Alibaba's Tmall offers a more tailored and brand-centric experience, which includes brands such as Gap, Nike, and Apple.
Supply Chain Management
While both Alibaba and Amazon are e-commerce giants, their supply chain strategies differ significantly. Amazon has vertically integrated its supply chain, owning and operating a vast logistics network of warehouses and delivery infrastructure. This allows Amazon to directly control the entire fulfillment process from storage to last-mile delivery.
In contrast, Alibaba takes an asset-light approach by connecting buyers and sellers on its platforms without owning inventory or logistics assets. Alibaba relies on third-party logistics providers and its logistics arm Cainiao to facilitate the movement of goods. This model enables Alibaba to rapidly scale its reach without the capital-intensive investments required for Amazon's vertically integrated model.
Common Queries Related to Alibaba and Amazon
What is the Main Difference between Alibaba and Amazon's business Models?
Which Company has a Stronger Focus on the B2B Market?
Which Company dominates the Chinese e-commerce Market?
Can Products Sourced from Alibaba be Sold on Amazon?
The Clash Continues
In this epic clash of the e-commerce titans, it's clear that both Alibaba and Amazon have carved out their respective domains of dominance. While Alibaba reigns supreme in its homeland of China and much of Asia, Amazon has established an iron grip over the Western markets, particularly in North America and Europe.
Yet, as these behemoths continue to expand their global footprints, the battleground is set for an even more intense showdown. With their contrasting business models, logistical prowess, and technological innovations, the future of online retail will undoubtedly be shaped by the strategies and maneuvers of these two giants.
Who will emerge victorious in this clash of the Titans? Only time will tell, but one thing is certain – the consumer is the ultimate winner in this high-stakes game of digital disruption.